ABSTRACT
We use a dataset of X-ray images from patients with common bacterial pneumonia, confrmed Covid-19 disease, and normal incidents, for the automatic detection of the Coronavirus disease.CNNs(Convolutional Neural Networks) are capable of extracting image features and are used for classification tasks extensively. We will be testing various CNN models fine tuned for our purpose (trained for 20 epochs) with the aim being to improve upon the performance of that of a single model by using certain techniques and observations and apply that to predict the final results.
Dataset
The dataset used is obtained from Kaggle. it contains 219 covid-19 confirmed X-Ray images along with images of normal and pneumonia X-Ray data around 1200 each. Out of this we choose equal number i.e 150 images from each category to train our models on , 20 images were used as validation data and the rest is used as test data as per requirement in my case 53+600+600. The directory structure for my data is available at github.
Transfer lerarning
We currently have many state of the art CNNs available that perform classification tasks efficiently. The aim here is to fine tune these models and get results and get the best model for out task. For all The models except Xception (pun intended) the images were rescaled to a size of 224X224 and for Xception it was 299X299.
The results obtained after fine tuning the popular CNN models used for classification are given below:
| Network | Accuracy(%) |
|---|---|
| VGG16 | 90.5027 |
| VGG19 | 92.6576 |
| MobileNetV2 | 91.3008 |
| ResNet50 | 92.0191 |
| Xception | 88.7470 |
Ensembling
Here we propose a model that take the average of the output prediction probabilities given by two base models for a given sample and predict the class according to this value. In simpler terms, in case the prediction given by two models differ, the image is classified according to the model that has higher probablility for its classification.
Here are some of the created ensembles:
| Ensemble | Accuracy(%) |
|---|---|
| VGG19 & ResNet50 | 93.0566 |
| VGG19 & VGG16 | 92.8970 |
| MobileNetV2 & VGG16 | 92.0191 |
| ResNet50 & MobileNetV2 | 93.2961 |
All of these seem to show increase in the accuracy as compared to their original base models. Particularly the ResNet50 & MobileNetV2 ensembles that gives better results than all the models.
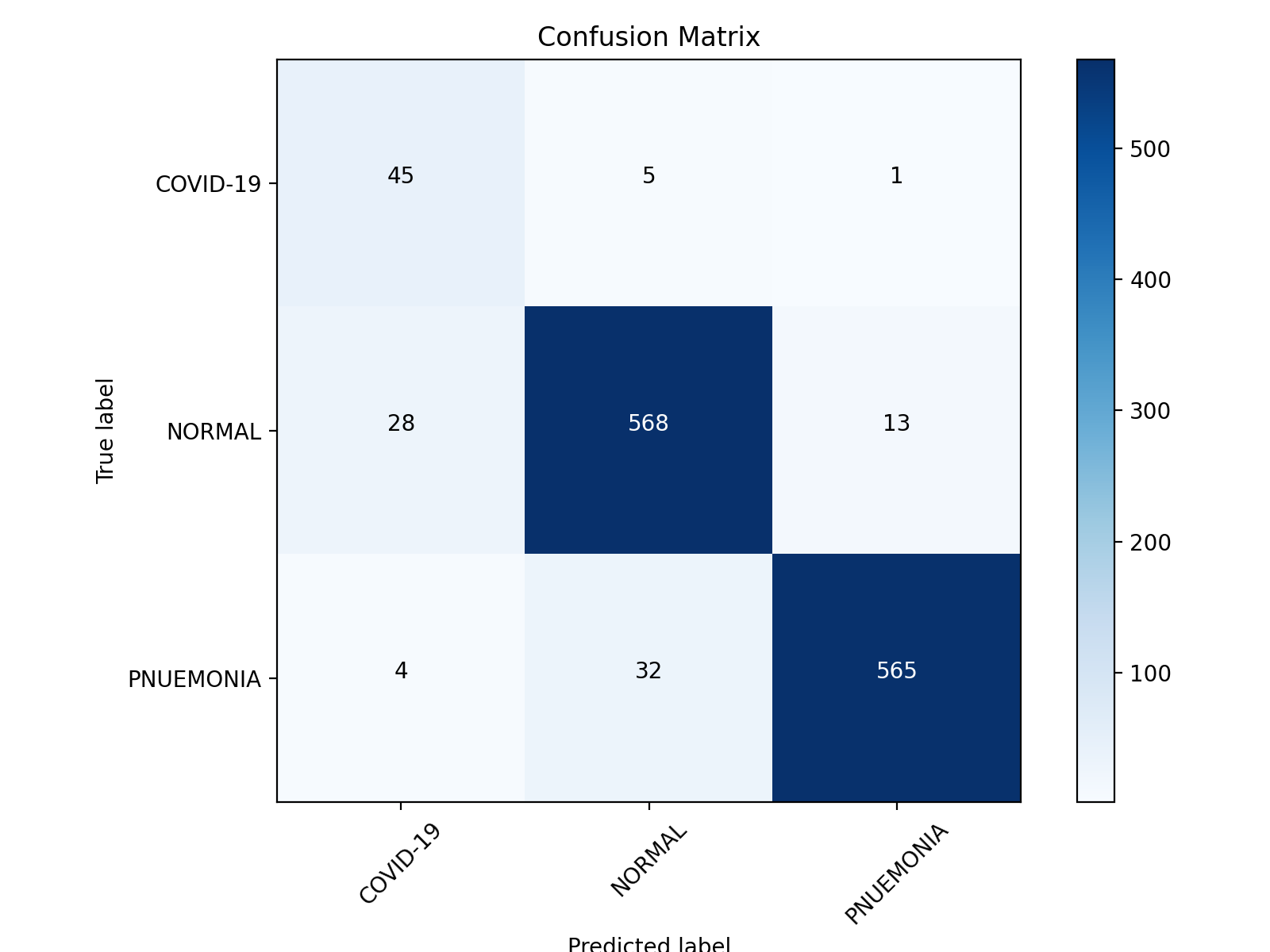
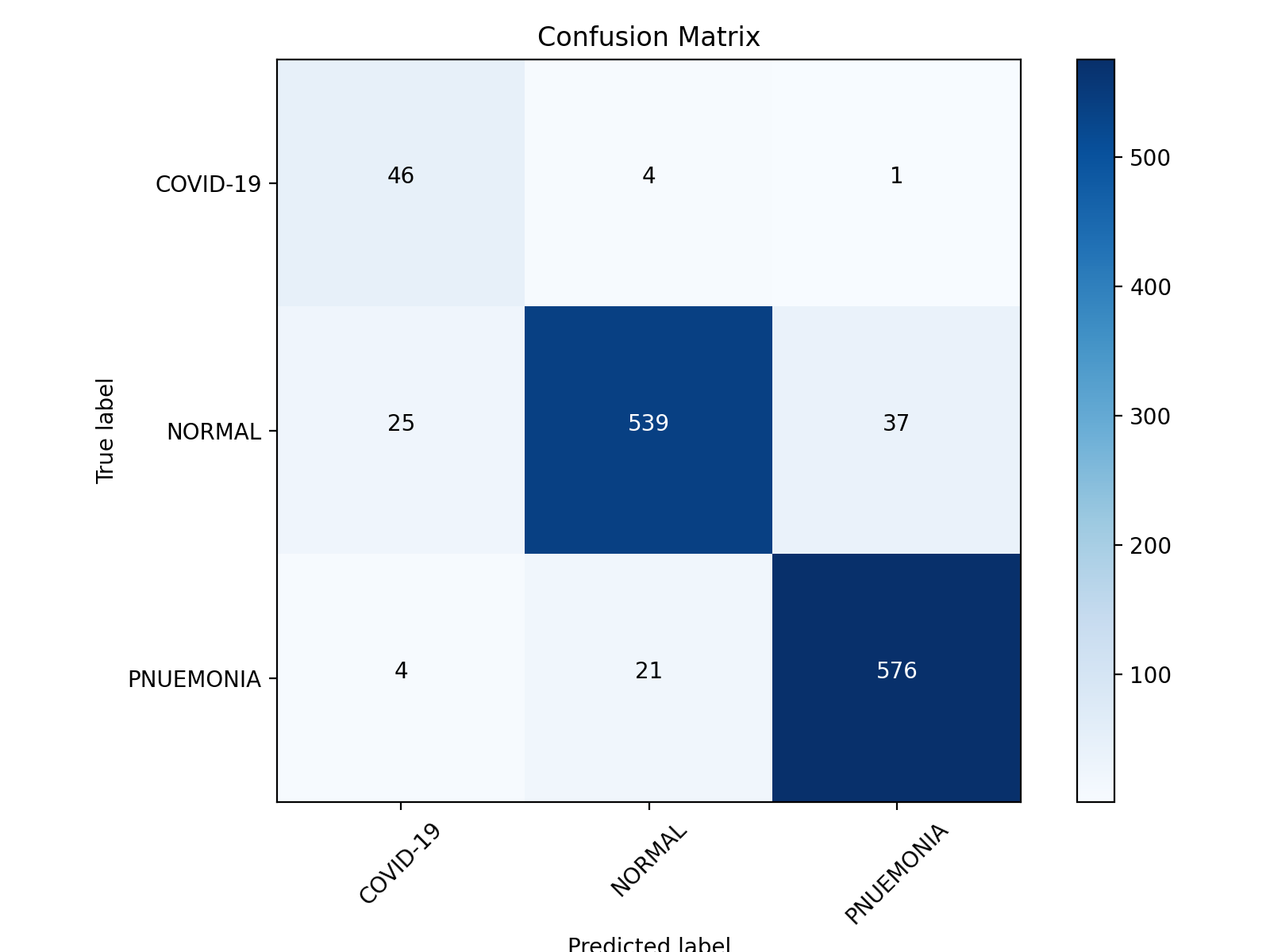 |
 |
|---|---|
| Confusion Matrix of VGG19 | Confusion Matrix of ResNet50 & MobileNetV2 ensemble |
Selective Combination
Now we make a new model with the prediction for normal class from the eansambled model and the rest from VGG19. Final Model:
The Proposed model gives us an Accuracy of 94.0144%
** All the above results were obtained from data on which the models were not trained on (out sample data). Now we are ready to use the model for prediction purpose: This can be found on my github repository along with all the required code and documentation for the same.
DISCUSSION
The proposed method is based on a very limited dataset where only 150 images were used to train a single category. Also the test data used was unblanced which does not affect the performance but may affect the precision of COVID class.
With around 150 trainig images we are able to get over 90% accuracy for Covid-19 detection among 2 other classes.
Based on the results, it is demonstrated that deep learning with CNNs may have signifcant efects on the automatic detection and automatic extraction of essential features from X-ray images, related to the diagnosis of the Covid-19.
it is necessary to develop models capable of distinguishing Covid-19 cases from other similar viral cases, such as SARS, but also from a greater variety of common pneumonia or even physiological X-rays.